GRP
high quality plastic for urban water management
GRP has been in use for more than 5 decades with a constantly increasing market share in the field of residential water management and demonstrably meets the highest demands for durability, safety, accuracy and economy.
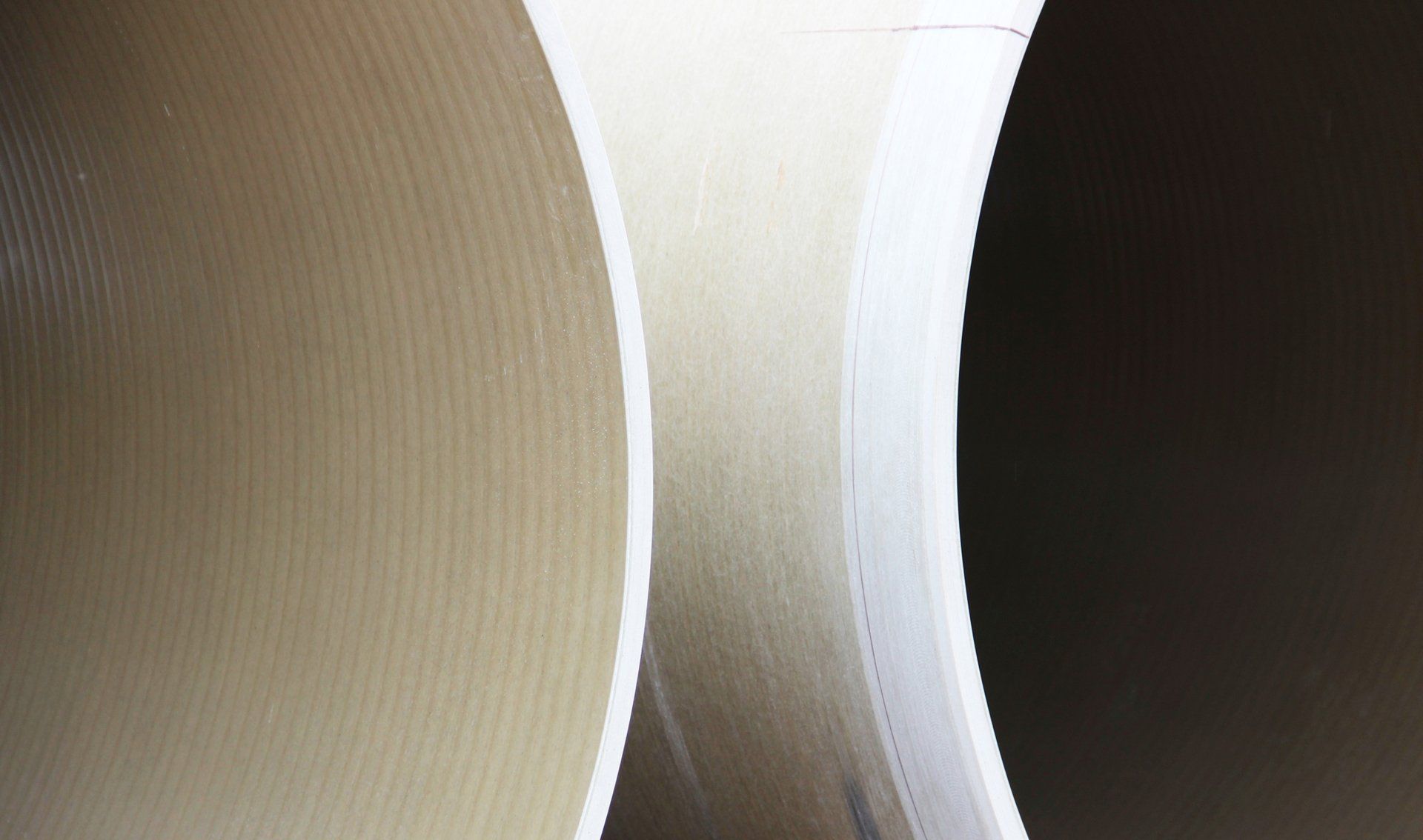

Pipe nominal diameter 4000 mm. Outside diameter: 4085 mm, inside diameter: 3966 mm, weight per running meter: 1650 kg.
Pipes and all necessary components can be produced in the required dimensions and shapes and connected by couplings or laminates. This results in high-quality plant components that guarantee a minimum service life of 50 years.
The rapid production and short construction time of plants offer further advantages. Since the 1970s, the material GRP has proven in practical and laboratory tests that it is resistant to corrosion due to aggressive components in waste water and is therefore excellently suited.
"Since the 1970s, GRP has proven in practical and laboratory tests that it is resistant to corrosion caused by aggressive components in waste water and is therefore excellently suited for this purpose".
The rapid production and short construction time of plants offer further advantages. Since the 1970s, the material GRP has proven in practical and laboratory tests that it is resistant to corrosion due to aggressive components in waste water and is therefore excellently suited.
QUALITY AND ADVANTAGES OF GRP
Low wall roughness (k < 0.01 to 0.029 mm)
excellent self-cleaning properties low adhesion of greases
Pressure classes from P1 to P 32
Deformability up to 40 % (6 % required)
pH value from pH 2 to pH 12
permanently resistant to (biogenic) acids / gases
Long-term test according to EN 1120
Minimum safety factor of 2.3 - 3.9 % (1.5 % required)
Ring stiffness SN 2,500 to 10,000
buried or in water, can be used for any traffic load
UV resistance
permanently
Guaranteed minimum service life
50 years
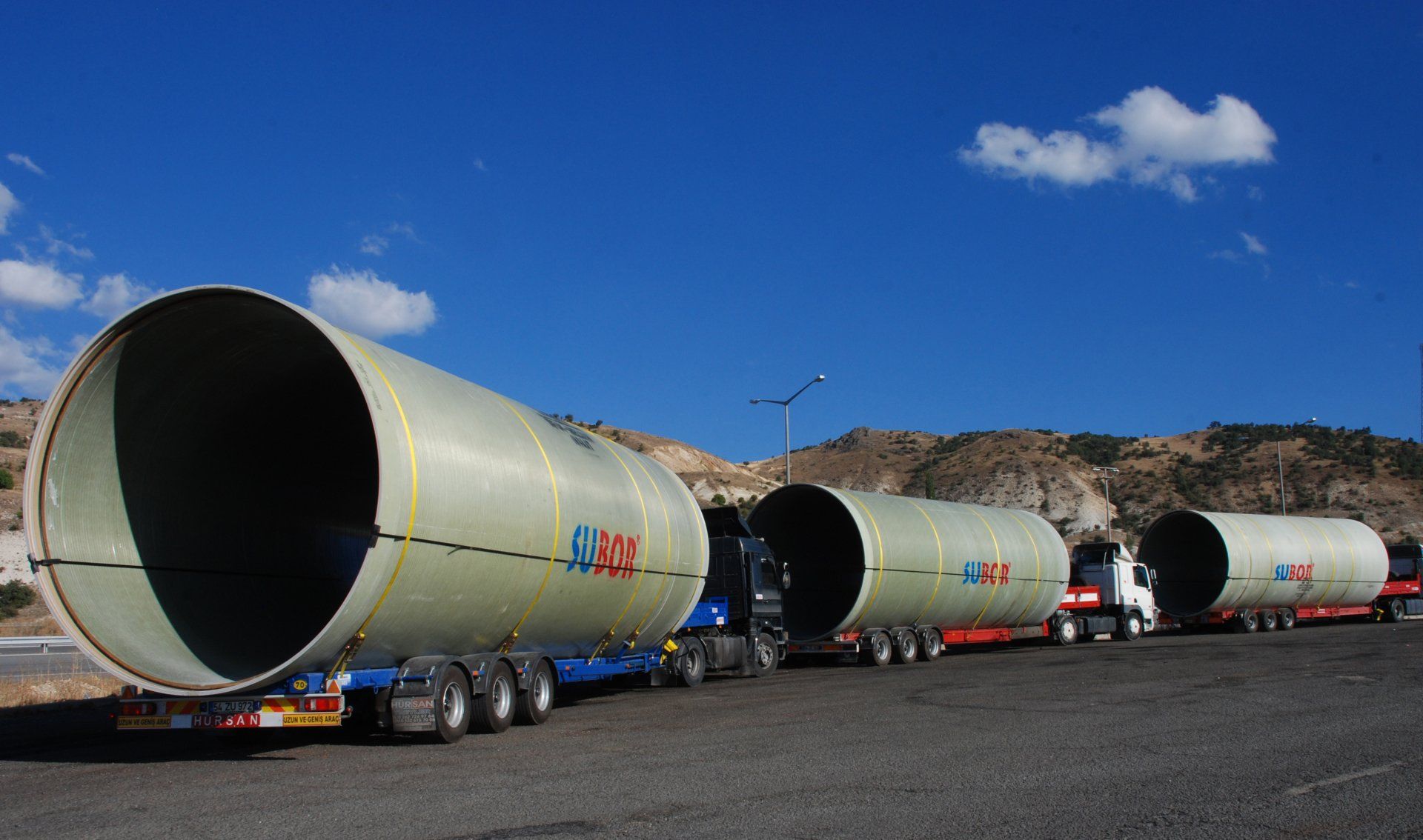

Tube 4000 mm on the way from the factory to the customer. (© Subor/Amiblue)
WALL CONSTRUCTION OF A GRP-PIPE
The laminate or wall structure consists of an outer and inner resin-rich layer, an inner and outer structural core and the middle structural core, the supporting laminate. The supporting laminate has a glass content of 50 - 70 %. Depending on the requirements of the client and the planning requirements, the individual layers of the GRP pipe can also be adapted in the production process for the intended purpose.
Production of GRP Pipes.
PRODUCTION AND COMPONENTS
GRP is a high-strength fiber composite material made of duroplastic plastics. GRP pipes for waste water disposal consist of unsaturated polyester resins - so-called "UP" according to DIN 18820 Part 3 - such as epoxy resin, which are manufactured in combination with highly resistant electrochemically resistant glasses "ECR glasses" and silicon oxide.
Glass is incorporated into the GRP element in three different ways: To withstand tension and elongation, it is used as continuous glass in the outer edge, as cut glass together with sand in the core of the tube. Glass fleece is used inside. The processing temperature in the factory is approx. 105 degrees, the epoxy resin can be processed up to a temperature of 230 degrees. GRP pipes do not contain plasticizers.
The consistently high, constantly testable quality is achieved by winding or centrifuging. The weather-independent manufacture of GRP pipes and components in the factory under standardized and strictly monitored production conditions guarantees maximum precision and enables a high level of manufacturing accuracy.
GRP is a high-strength fiber composite material made of duroplastic plastics. GRP pipes for waste water disposal consist of unsaturated polyester resins - so-called "UP" according to DIN 18820 Part 3 - such as epoxy resin, which are manufactured in combination with highly resistant electrochemically resistant glasses "ECR glasses" and silicon oxide.
"The weather-independent production of GRP tubes and components in the factory under standardized and strictly monitored production conditions guarantees the highest precision and enables high quality manufacturing accuracy."
Glass is incorporated into the GRP element in three different ways: To withstand tension and elongation, it is used as continuous glass in the outer edge, as cut glass together with sand in the core of the tube. Glass fleece is used inside. The processing temperature in the factory is approx. 105 degrees, the epoxy resin can be processed up to a temperature of 230 degrees. GRP pipes do not contain plasticizers.
The consistently high, constantly testable quality is achieved by winding or centrifuging. The weather-independent manufacture of GRP pipes and components in the factory under standardized and strictly monitored production conditions guarantees maximum precision and enables a high level of manufacturing accuracy.
DURABILITY AND CORROSION
In the period from 1970 to 2005, the chemical resistance of GRP pipes was investigated in a long-term test. The specimens were permanently subjected to tensile elongation in the pipe bottom under bending load and a 5% sulphuric acid concentration in accordance with EN 1120 and ISO 10952 (unchanged basis is ASTM D3681 of 1978).
The analysis of almost 650 samples after 28 years allows the extrapolation that GRP pipes will maintain a much higher safety factor after 150 years than is required for applications in residential water management. The required minimum safety factor is 1.5, while GRP reaches values of 2.3 to 3.9.
In the period from 1970 to 2005, the chemical resistance of GRP pipes was investigated in a long-term test. The specimens were permanently subjected to tensile elongation in the pipe bottom under bending load and a 5% sulphuric acid concentration in accordance with EN 1120 and ISO 10952 (unchanged basis is ASTM D3681 of 1978).
"GRP pipes in accordance with DIN EN14364 are permanently resistant to concrete structures and corrosion-resistant to biogenic hydrogen sulphide. A special layer to protect against corrosion is therefore not necessary."
The analysis of almost 650 samples after 28 years allows the extrapolation that GRP pipes will maintain a much higher safety factor after 150 years than is required for applications in residential water management. The required minimum safety factor is 1.5, while GRP reaches values of 2.3 to 3.9.
GRP pipes in accordance with DIN EN14364 are permanently resistant to concrete structures and corrosion-resistant to biogenic hydrogen sulfide. A special layer to protect against corrosion is therefore not necessary.
CO2 emissions
Although the CO2 emission of 1.35 t from the production of GRP pipes is higher than that of concrete (0.26 t), the emission is put into perspective in a direct comparison of structures, as GRP storage basins require considerably thinner walls for the same static loads. If a concrete basin requires a wall thickness of 40 cm for the side walls or 50 cm for the base plate, the same storage chamber can be used with a GRP pipe with a maximum wall thick-ness of 5.6 cm. If, for example, 2 tanks with a volume of 400 m3 capacity are compared, where one was built from GRP and one from concrete, the result for the concrete tank is a CO2 emission of 72.95 t, for the GRP tank a CO2 emission of 49.01 t. The same applies to the GRP tank. GRP is therefore not only an excellent structural alternative, the high-tech construction material also makes an outstanding contribution to environmental protection.
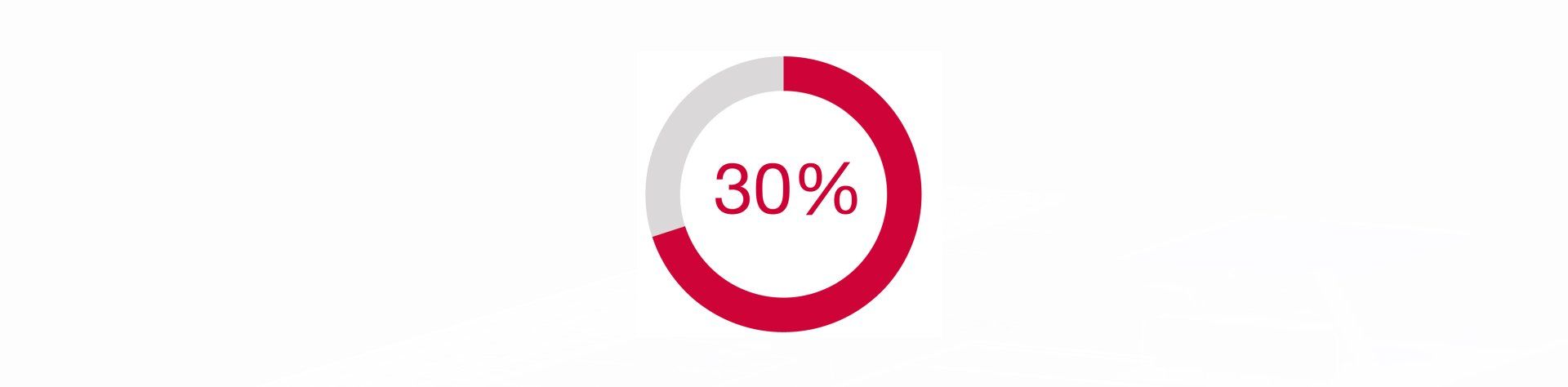
With the same basin sizes, CO2 emissions can be reduced by 30% or more compared to concrete basins by using GRP pipes.
SPECIAL SHAPES AND DIAMETERS
In addition to pipes with diameters from 600 mm to 4000 mm in various strength classes, all fittings required in pipeline construction are manufactured in series. Manholes, domes and other large-format fittings are joined to the pipes in the factory or on site by lamination with a GRP mesh and resins. This eliminates the need for costly material changes and screw connections and the associated technical and economic risks. High-end systems are created from a single "casting".
The connection between the individual pipe segments is realized by the manufacturer coupling with inserted EPDM seal, which has proven itself in decades of practice, or can be realized e.g. by stainless steel couplings of other manufacturers.
In addition to pipes with diameters from 600 mm to 4000 mm in various strength classes, all fittings required in pipeline construction are manufactured in series. Manholes, domes and other large-format fittings are joined to the pipes in the factory or on site by lamination with a GRP mesh and resins. This eliminates the need for costly material changes and screw connections and the associated technical and economic risks. High-end systems are created from a single "casting".
The connection between the individual pipe segments is realized by the manufacturer coupling with inserted EPDM seal, which has proven itself in decades of practice, or can be realized e.g. by stainless steel couplings of other manufacturers.
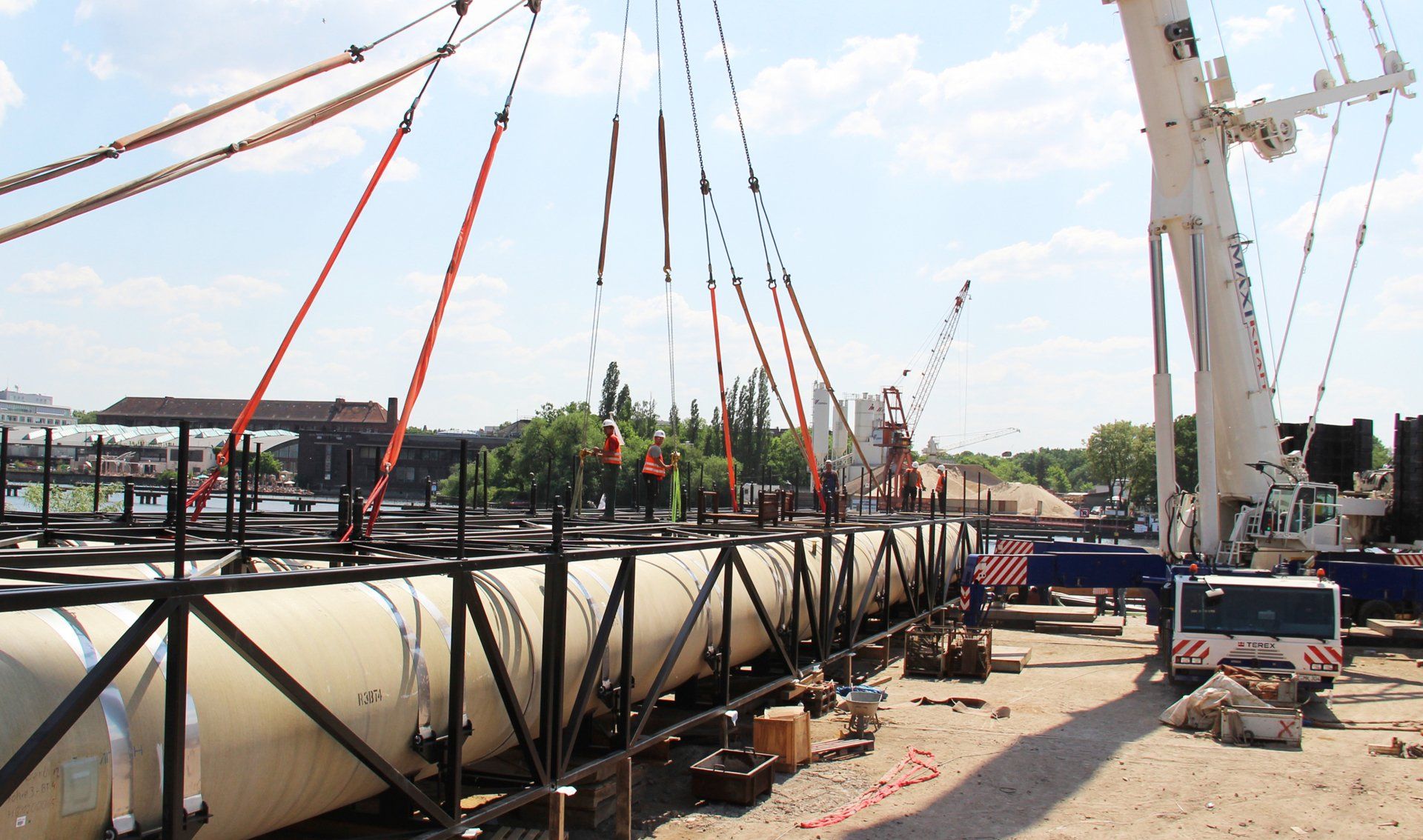

Pipe 2000 mm before installation under water.
STATIC VERIFICATION AND DEFORMATION
The quartz sand used contributes to the wall structure and thus also to the increase in stiffness. In tests, deformations of up to 40 % were necessary before fracture occurred. Likewise, the high-precision couplings with elastomeric seals did not suffer any damage during these tests. Even in the long-term behavior under continuous load - e.g. under heavily trafficked roads with additional temperature changes - GRP pipes show excellent properties with regard to deformation and fracture. This applies to all freely selectable pressure classes from PN 1 to PN 32. According to ATV A-127, the static verification for GRP pipes up to pressure class P 32 is verified for each project.
The use of glass fibres not only achieves high rigidity and thus reduces the inherent deformation, but also prevents the formation of cracks and fractures.
"Even in long-term behaviour under continuous load - e.g. under heavily trafficked roads with additional temperature changes - GRP pipes show excellent properties in the areas of deformation and fracture."
The quartz sand used contributes to the wall structure and thus also to the increase in stiffness. In tests, deformations of up to 40 % were necessary before fracture occurred. Likewise, the high-precision couplings with elastomeric seals did not suffer any damage during these tests. Even in the long-term behavior under continuous load - e.g. under heavily trafficked roads with additional temperature changes - GRP pipes show excellent properties with regard to deformation and fracture. This applies to all freely selectable pressure classes from PN 1 to PN 32. According to ATV A-127, the static verification for GRP pipes up to pressure class P 32 is verified for each project.
ABRASION RESISTANCE
GRP is abrasion-resistant according to DIN EN 295-3, the Darmstadt method. The 100,000 load cases carried out using the tilting method with sand certify a standard-compliant durability of 50 - 80 years. In hazardous areas, e.g. in the area of the pump suction nozzle or jet nozzles, it is possible to build up an additional wear protection layer by using quartz sand and resin-rich liner layers which are provided with appropriate additives.
WALL ROUGHNESS
The very low wall roughness is k < 0.01 to 0.029 mm. This is therefore considerably lower than with concrete pipes (k= < 0.1 mm). This gives the GRP pipes excellent self-cleaning properties.
GRP is abrasion-resistant according to DIN EN 295-3, the Darmstadt method. The 100,000 load cases carried out using the tilting method with sand certify a standard-compliant durability of 50 - 80 years. In hazardous areas, e.g. in the area of the pump suction nozzle or jet nozzles, it is possible to build up an additional wear protection layer by using quartz sand and resin-rich liner layers which are provided with appropriate additives.
WALL ROUGHNESS
The very low wall roughness is k < 0.01 to 0.029 mm. This is therefore considerably lower than with concrete pipes (k= < 0.1 mm). This gives the GRP pipes excellent self-cleaning properties.
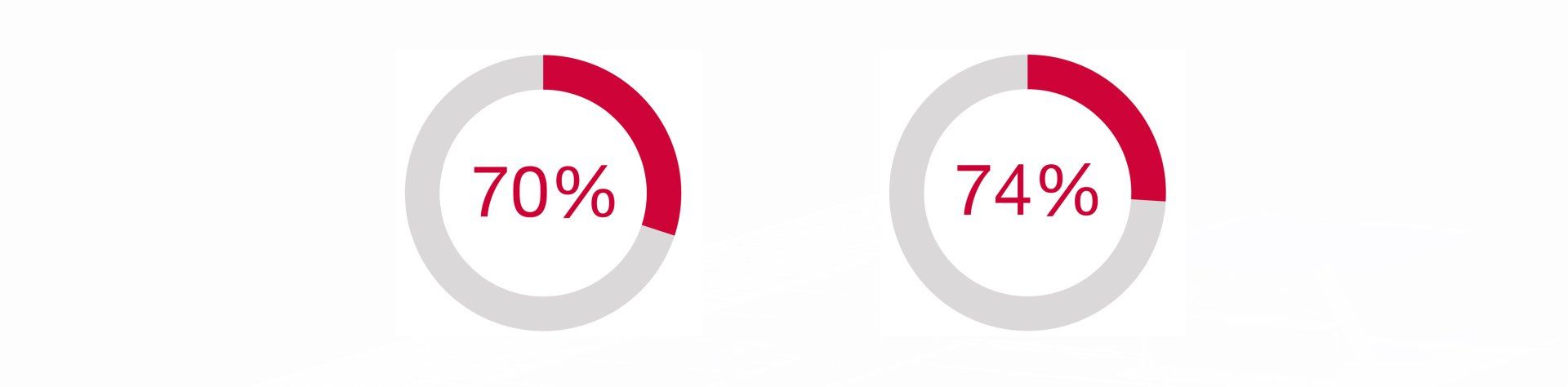
Lower weight: Due to the up to 70 % lower weight compared to concrete pipes, even large pipe lengths and diameters can be moved with the excavator. If necessary, the building of construction roads can be avoided.
The surface of GRP pipes is up to 74% smoother than that of concrete pipes. This reduces adhesion and deposits in the pipe and thus the operating costs.
The surface of GRP pipes is up to 74% smoother than that of concrete pipes. This reduces adhesion and deposits in the pipe and thus the operating costs.
FLAMMABILITY
GRP and GRP laminates are only flammable at high temperatures. If required (e.g. in bridge construction), flammability class 2 can be achieved by adding aluminum hydroxide. Oxidation causes it to form water in the event of a fire and thus cools the process automatically.
GRP and GRP laminates are only flammable at high temperatures. If required (e.g. in bridge construction), flammability class 2 can be achieved by adding aluminum hydroxide. Oxidation causes it to form water in the event of a fire and thus cools the process automatically.

Numbering for seamless quality assurance.
UV RESISTANCE
GRP pipes are UV resistant. If the material is used above ground and is therefore exposed to sunlight, it is guaranteed that the structural integrity and UV resistance of the pipes will not change.
OSMOSIS
Osmosis or osmotic pressure occur when the prescribed processing temperatures have not been maintained or chemical components in the laminate have not reacted with the resin. Inclusions of highly concentrated resin components and surrounding "less" concentrated water diffuse into the material through concentration compensation. This physical process creates osmotic pressure which, depending on the ambient conditions, can lead to the formation of bubbles.
In order to rule this out, a high processing and hardening temperature of 110 degrees Celsius is maintained during production. In reaction resin systems, errors in the mixing ratio of the resin components, low processing or hardening temperatures or binders can be a cause of osmosis.
Osmosis does not occur in the GRP pipes we use. The guaranteed adherence to the mixing ratios and processing temperatures as well as a perfect, constantly controlled composition of the resin is an essential aspect which the manufacturer strictly adheres to.
GRP pipes are UV resistant. If the material is used above ground and is therefore exposed to sunlight, it is guaranteed that the structural integrity and UV resistance of the pipes will not change.
OSMOSIS
Osmosis or osmotic pressure occur when the prescribed processing temperatures have not been maintained or chemical components in the laminate have not reacted with the resin. Inclusions of highly concentrated resin components and surrounding "less" concentrated water diffuse into the material through concentration compensation. This physical process creates osmotic pressure which, depending on the ambient conditions, can lead to the formation of bubbles.
In order to rule this out, a high processing and hardening temperature of 110 degrees Celsius is maintained during production. In reaction resin systems, errors in the mixing ratio of the resin components, low processing or hardening temperatures or binders can be a cause of osmosis.
Osmosis does not occur in the GRP pipes we use. The guaranteed adherence to the mixing ratios and processing temperatures as well as a perfect, constantly controlled composition of the resin is an essential aspect which the manufacturer strictly adheres to.
REPAIRS AND CONVERSIONS
If damage is caused by external influences and improper handling, or if conversions are necessary at a later date, these can be easily carried out using laminates.
RECYCLING
In Germany, GRP waste pipe material is sent to domestic waste dumps; it is not hazardous waste. A separation into the individual components is not technically possible at present. The energetic utilization of the contained resins requires more activation energy than can be obtained from it due to their quartz sand content.
HANDLING ON THE CONSTRUCTION SITE
The relatively low weight of even large GRP components enables good handling on the construction site. Pushing pipes together with the help of an excavator is relatively quick and the laying capacity can be up to 120 m pipe / day. The manufacturer sets a time of 1 to 4 hours for the installation of a single GRP element.
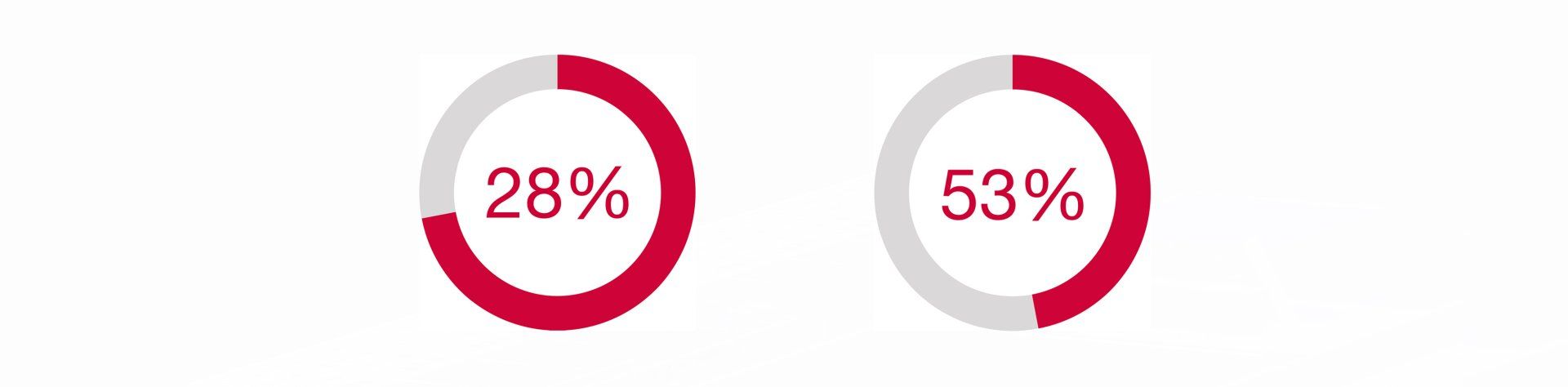
Considerable cost reduction: Basins made of GRP pipes enable costs to be reduced by up to 28% compared with similar concrete systems.
Faster construction time: When installing basins with GRP pipes, time savings of up to 53% are possible compared to conventional concrete basins.
Faster construction time: When installing basins with GRP pipes, time savings of up to 53% are possible compared to conventional concrete basins.
All specifications must be checked.
Continue with about us
EXAMPLES OF GRP-MANUFACTURERS
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=udGJN3Yo-lc
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qH31XvJGAUc
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=udGJN3Yo-lc
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qH31XvJGAUc

